Earmolds and fittings are an essential service for the health of the ear. While we do provide custom molds to fit hearing aids, we also do fittings for sound plugs, earpieces, earbuds and plugs for swimming, watching sports, listening to music, working, shooting and other activities.
 Hearing aids come in shapes and sizes as unique as people’s ears. We offer a variety of earmold styles including canal earmolds, which are made to fit inconspicuously in the ear canal; full-shell earmolds, which are built to prevent feedback and falling out; half-shell earmolds, which only cover the bottom half of the concha bowl; skeleton earmolds, designed for comfort and semi-skeleton earmolds, similar to skeleton but without the back ring. Each of these styles is custom-molded to the patient’s ear for comfort and effectiveness.
Hearing aids come in shapes and sizes as unique as people’s ears. We offer a variety of earmold styles including canal earmolds, which are made to fit inconspicuously in the ear canal; full-shell earmolds, which are built to prevent feedback and falling out; half-shell earmolds, which only cover the bottom half of the concha bowl; skeleton earmolds, designed for comfort and semi-skeleton earmolds, similar to skeleton but without the back ring. Each of these styles is custom-molded to the patient’s ear for comfort and effectiveness.
We also mold sound plugs and swimmer’s plugs to help protect the ears. People who have jobs in noisy locations, such as airports and construction sites, benefit from custom-fit sound plugs to prevent damage caused by noise exposure. Swimmers need earplugs to prevent water blockage, which can cause temporary hearing loss.
Others who may be at less risk for occupational hearing loss can still benefit from having custom-molded ear equipment. For example, musicians and shooters may have custom-molded noise-cancelling ear plugs, and office workers may benefit from custom earpieces for their phones. The purpose of these custom fittings is to provide comfort for the patient.
To learn more about our custom earmolds and fittings, contact us at (479) 750-2080. Our goal is to care for our patients’ whole hearing health.
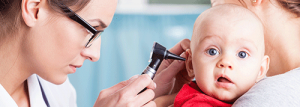 Pediatric audiology is the study and treatment of hearing loss in infants, toddlers, and children. Our experts evaluate and treat children of all developmental stages. Our goal is to detect and treat hearing loss in children as early as possible. Since our audiologists work closely with our physicians, we can care for your child’s whole hearing health.
Pediatric audiology is the study and treatment of hearing loss in infants, toddlers, and children. Our experts evaluate and treat children of all developmental stages. Our goal is to detect and treat hearing loss in children as early as possible. Since our audiologists work closely with our physicians, we can care for your child’s whole hearing health.
Hearing is essential for babies’ and young children’s development. It is especially important to treat deafness in children so that they can cultivate essential speech and communication skills during the developmental years. This is why we focus on early detection and treatment of hearing loss.
We offer the same audiology services for children as we do adults. However, we recognize that children respond differently to testing and may have less ability than adults to focus or respond to stimuli. We therefore incorporate a more fun and caring approach with children.
For children old enough to follow instructions and respond to sounds, we use the following testing methods made to feel like games: visual reinforcement audiometry, conditioned play audiometry, speech audiometry (word recognition) and auditory processing testing. Physiological tests are used for infants who cannot respond to behavioral tests. These include otoacoustic emissions and acoustic reflex testing.
Fitting a hearing aid to a growing child’s ear is different than with an adult. We have the technology, equipment and training to make sure each child has properly fitting hardware through each stage of life.
If you suspect hearing loss in your child, contact us at (479) 750-2080 for more information.
Tinnitus is described as an irritating buzzing, humming or ringing in the ears. What many don’t realize is that it is usually a symptom of a greater problem rather than a disease itself. The first step to tinnitus management is to diagnose the underlying issue.
Some common causes of tinnitus include impacted wax in the external ear, an infection, middle ear or nerve tumors, circulation disorders, noise-induced hearing loss of the inner ear, migraines and epilepsy. It is important to see an audiologist for tinnitus symptoms in order to identify or prevent hearing loss.
Tinnitus is impossible to evaluate objectively. The doctor will ask a series of questions such as which ear is experiencing the symptoms, whether or not it is constant, if you can describe it, how loud does it seem, what conditions affect it or make it worse and how much it disrupts your daily life.
Usually tinnitus is merely an irritation, but it also can be a symptom or cause of hearing loss. Audiologists can work with other ENT doctors to determine if a hearing aid is necessary. Hearing aids and tinnitus maskers can work together to both override tinnitus symptoms with more tolerable sounds and assist with regular hearing.
It is best to treat the underlying cause of tinnitus, but the cause cannot always be determined. This means there is not always a specific cure. Some alternative treatment options include hypnosis, counseling, relaxation therapy, biofeedback and tinnitus maskers, which are like hearing aids or white noise machines. Self-help groups are another option for those suffering from mild forms of tinnitus. They can provide resources and support to help people feel more in control. Your audiologist can help determine what treatment option is best for you.
A bone-anchored hearing device is a specific type of surgically implanted hearing aid that works by transmitting soundwaves directly through the skull rather than through the ear. The bone-anchored hearing device consists of three parts: a titanium fixture, an abutment and an external sound processor. The fixture is surgically implanted into the bone behind the ear so that only the titanium abutment is visible. The sound processor, which “catches” the vibrations of sound waves, transfers the waves through the abutment into the bone and then to the inner ear. It allows the user to still hear sounds naturally, similar to how one hears their own voice.
Bone-anchored hearing devices are best suited for those with conductive hearing loss, unilateral hearing loss, single-sided deafness or mixed hearing loss due to damages to the middle or outer ear. This is because the bone-anchored hearing device system bypasses these features and transfers sound directly from outside the head into the inner ear.
The implantation is a minor surgery which takes only about one hour. The doctor will provide either local or general anesthesia before performing an incision behind the ear with hearing loss. A small hole three to four millimeters deep is drilled so that the titanium fixture and abutment can be inserted, then the skin is sewn snugly around the fixture. There can be minor post-operative pain or discomfort, but most patients can go back into their daily routines within just a few days.
It is possible to test the bone-anchored hearing device system to see if it will work for you. Your doctor can connect the bone-anchored hearing device sound processor to your head via headband, which will provide a similar hearing experience to the implant.
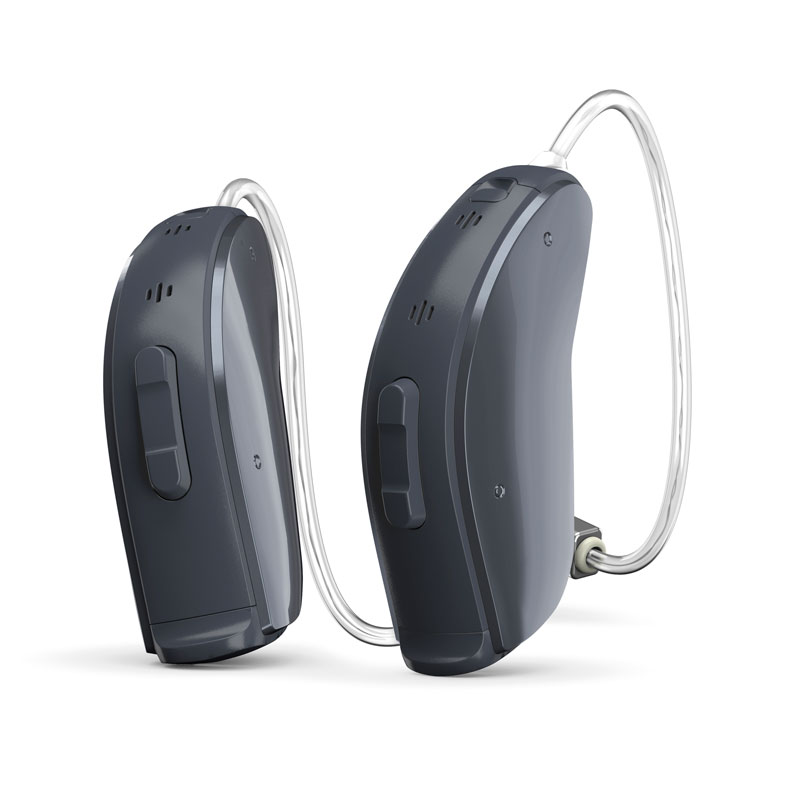 Hearing aids are devices designed to help those with hearing loss hear, process and understand sound. There are many types of hearing aids such as behind-the-ear aids, in-the-ear aids, invisible in-canal hearing aids, extended-wear hearing aids, open-fit devices and bone-anchored hearing aids. Each works differently and is recommended by a doctor based on the patient’s degree of hearing loss, lifestyle and preference.
Hearing aids are devices designed to help those with hearing loss hear, process and understand sound. There are many types of hearing aids such as behind-the-ear aids, in-the-ear aids, invisible in-canal hearing aids, extended-wear hearing aids, open-fit devices and bone-anchored hearing aids. Each works differently and is recommended by a doctor based on the patient’s degree of hearing loss, lifestyle and preference.
Choosing a Hearing Aid
Once you’ve seen an audiologist and been tested for hearing loss, your doctor may decide you could benefit from hearing aids. There are a wide variety of hearing aid manufacturers and types of hearing aids, which may make the process of choosing a hearing aid seem overwhelming. There are three major questions to consider when…
Read More
Hearing Aid Styles
Although there are many types of hearing aids, the five major styles are completely-in-canal (CIC), in-the-canal (ITC), in-the-ear (ITE), behind-the-ear (BTE) and Receiver-in-the-Ear (RITE). You and your audiologist can discuss which style is best for you in terms of appearance and functionality. Completely-in-canal (CIC) or mini-CIC are devices that are molded to fit completely inside…
Read More
Hearing Aid Accessories
Hearing aids aren’t just available in a wide range of sizes and styles; they can also accommodate a variety of accessories. Deciding which, if any, will benefit you can be tricky. You may want to speak with an audiologist to learn more about any particular product. Some of the more popular hearing aid accessories include:…
Read More
Hearing Aid Maintenance & Repair
Though small, hearing aids are packed with high-level technology to help your ears and brain process sounds. As such, there are several practices that will help you care for the technology so that it will last. To prevent problems with your hearing aids, follow this list of practices to help preserve the device’s technology. o…
Read More
Hearing Aid Batteries
Without batteries, your hearing aids wouldn’t be unable to function. To keep your devices running as smoothly as possible without interruption, there are a few things to know about hearing aid batteries. Most drugstores carry replacement batteries; they can also be purchased from your audiologist or ordered online. Most hearing aids use disposable zinc-air batteries…
Read More
Hearing Aid Financing
Our goal is for you to obtain the most benefit at the lowest price. We provide a wide variety of aids that range in price from $1000 to $3000 per ear. A three-year manufacturer’s warranty is included in the cost of the aid(s). Hearing aids come with a 30-day trial. When hearing aids are ordered…
Read More
Hearing Aid Travel Tips
Traveling can cause stress for those with hearing loss. There are certain measures you can take to ensure your hearing aids are safe and your traveling experience is stress-free. Here is a list of tips for traveling with hearing aids: Pack extra batteries and tubing. These things may be difficult to find depending on where…
Read More
Bone Anchored Hearing Devices
A bone-anchored hearing device is a special type of implanted hearing aid that works by transmitting soundwaves directly through the skull rather than through the ear. The bone-anchored hearing device consists of three parts: a titanium fixture, an abutment and an external sound processor. The fixture is surgically implanted into the bone behind the ear…
Read More
Tinnitus
Tinnitus is described as an irritating buzzing, humming or ringing in the ears. What many don’t realize is that it is may be a symptom of a greater problem rather than a disease itself. The first step to treating tinnitus is to diagnose the underlying issue. Some common causes of tinnitus include hearing loss, an…
Read More
More than 48 million Americans have some degree of hearing loss. There are three major types of hearing loss, but every individual’s experience is affected by different factors, such as genetics, age and exposure to noise.
The three types of hearing loss are conductive, sensorineural and mixed. Conductive hearing loss is may be due to problems with the ear canal, eardrum or middle ear that prevent sound from passing through the ear. Sensorineural hearing loss is may be caused by problems with the inner ear (the cochlea) or the nerves coming from the cochlea, which senses sound waves and sends them to the brain for processing. Mixed hearing loss is a combination of both conductive and sensorineural. Our clinicians will determine what type of hearing loss you are experiencing and develop an effective and specialized treatment plan for your unique hearing needs.
Symptoms of hearing loss can go unnoticed if you don’t know what to look for. A very common symptom is difficulty hearing in noisy settings such as at a restaurant or party. Other symptoms include frequently asking people to repeat themselves, ringing in the ears, turning up the TV or radio volume louder than others need it and withdrawing from conversations. In children, symptoms of hearing loss may include not responding to noises, speaking unclearly and not following simple commands.
If you experience sudden deafness due to a loud noise or any other reason, you should seek immediate medical attention. While most hearing loss is gradual, one can have a sudden hearing loss. This can be an emergency.
Please contact us at (479) 750-2080 to schedule an appointment if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of hearing loss.
The process of hearing requires interaction between the ears and the brain. Hearing tests determine whether or not the two are working together, and if not, what exactly needs to be fixed.
Sound waves travel through the ear canal and into the eardrum. These waves move at a certain speed (frequency) and have a certain height (amplitude). Faster frequencies emit a higher pitch, and taller waves produce louder sounds. These characteristics translate to nerve impulses, which then are sent to the brain. This is the process of hearing.
There are many types of hearing tests that determine what kind of hearing deficiency a patient has. Different testing methods are used depending on the patient’s age, the doctor’s concerns and other factors.
 One of the most common hearing testing methods in adults and older children is pure-tone audiometry testing. This test determines what volume of sound a patient can hear at different frequencies. This test is usually conducted with headphones, but sometimes a sound booth is used. The doctor presents a tone through the speakers, and the patient indicates whether or not they can hear it. This test establishes whether a patient is impaired from hearing specifically high or low tones.
One of the most common hearing testing methods in adults and older children is pure-tone audiometry testing. This test determines what volume of sound a patient can hear at different frequencies. This test is usually conducted with headphones, but sometimes a sound booth is used. The doctor presents a tone through the speakers, and the patient indicates whether or not they can hear it. This test establishes whether a patient is impaired from hearing specifically high or low tones.
A variation of pure-tone audiometry testing is speech testing, sometimes referred to as “whispered speech test.” The concept is the same, except instead of tones, the audiologist will say or play words at quieter and quieter specific volumes to determine at what point the patient can no longer hear soft noises and discriminate between common sounds used in speech.
Ear, nose and throat concerns are among the top reasons children go to see their doctors. This is because children are especially sensitive to issues like ear infections and food allergies, and because certain birth defects such as cleft palates must be treated at a young age to prevent complications when older. The best way to treat ENT disorders in children is to bring them to an ENT clinic where multiple specialists work in close collaboration to care for your child’s total well-being.
 Common ENT issues that affect children are tonsil infections, sinus infections, hearing loss, snoring, sleep apnea, stridor (noisy breathing), infections of the lymph nodes, epistaxis (nose bleeding), chronic cough, voice disorders, nasal blockage and allergies.
Common ENT issues that affect children are tonsil infections, sinus infections, hearing loss, snoring, sleep apnea, stridor (noisy breathing), infections of the lymph nodes, epistaxis (nose bleeding), chronic cough, voice disorders, nasal blockage and allergies.
Ear, Nose & Throat Center of the Ozarks offers the same services for children as we do adults including a broad range of medical and surgical treatments, allergy testing, allergy shots, allergy drops, hearing testing, hearing aids, speech therapies and more. What sets our pediatric services apart is our ability to incorporate gentle and stimulating techniques to engage and comfort children while evaluating and treating them. We understand that children require a special kind of care, which is why we strive to minimize pain, discomfort and anxiety in our child patients.
If you suspect ENT-related problems in your child, please contact us at (479) 750-2080. Our expert clinicians will give you peace of mind with their specialized care.
The thyroid and parathyroid are endocrine glands near the throat that secrete hormones throughout the body. The thyroid is bowtie-shaped and rests in front of the trachea (windpipe). It uses iodine from food to regulate the body’s energy and metabolism. The parathyroid is a cluster of glands generally located behind the thyroid. They control the amount of calcium that stays in the bloodstream. Dr. Manning’s busy thyroid and parathyroid practice performs hundreds of biopsies and thyroidectomies per year.
Thyroid/Parathyroid Disease
The thyroid and parathyroid are endocrine glands near the throat that secrete hormones throughout the body. The thyroid is bowtie-shaped and rests in front of the trachea (windpipe). It uses iodine from food to regulate the body’s energy. The parathyroid is a cluster of smaller glands located on the back of the thyroid. Their role…
Read More
Ultrasound Guided Biopsy
An ultrasound-guided biopsy uses soundwave imaging to guide a needle into the thyroid tumors or other tumors of the head or neck and remove a small tissue sample. This procedure is generally much safer and less invasive than a surgical biopsy. The procedure normally takes less than thirty minutes. It can be performed with local…
Read More
Thyroid nodules
Thyroid nodules are lumps or cysts that form in the thyroid. Many are simply an overgrowth of normal thyroid tissue. These lumps can be buried deep in thyroid tissues or may be located near the edge and feel like a lump in the skin. In some cases, they can even be visible in the front…
Read More
Thyroid/Parathyroid Surgery
The thyroid and parathyroid are endocrine glands near the throat that secrete hormones throughout the body. The parathyroid is a cluster of smaller glands located near the back of the thyroid that controls the amount of calcium in the blood. There are three major reasons that the thyroid or parathyroid would need to be surgically…
Read More
The longest a human has survived without sleep is 264 hours, or 11 days. Sleeping is like eating and breathing – it is an essential human function. When you sleep, your body works to maintain your health; in particular, it maintains the health of your brain. During sleep, your body forms new pathways to help you learn information the next day. It also solidifies both short and long-term memories from the previous days. If you have trouble falling or staying asleep, your physical, mental and emotional health are at risk. Dr. Manning is triple board certified, one of which is in sleep medicine.
Snoring/Sleep Apnea
As many as forty-five percent of adults report occasional snoring, and over twenty-five percent snore every night. Snoring occurs when there is an obstruction in air flow in the throat, mouth and/or nose. The sound we hear is the result of the tongue or upper throat vibrating against the soft palate and uvula during breathing.…
Read More
Sleep Treatment
CPAP A continuous positive airway pressure device (CPAP) is a treatment option for those with sleep apnea or other breathing problems. The CPAP consists of three major parts: a mask that fits over the mouth and nose with straps to hold it in place, a tube that connects the mask to the motor and the…
Read More
 Hearing aids come in shapes and sizes as unique as people’s ears. We offer a variety of earmold styles including canal earmolds, which are made to fit inconspicuously in the ear canal; full-shell earmolds, which are built to prevent feedback and falling out; half-shell earmolds, which only cover the bottom half of the concha bowl; skeleton earmolds, designed for comfort and semi-skeleton earmolds, similar to skeleton but without the back ring. Each of these styles is custom-molded to the patient’s ear for comfort and effectiveness.
Hearing aids come in shapes and sizes as unique as people’s ears. We offer a variety of earmold styles including canal earmolds, which are made to fit inconspicuously in the ear canal; full-shell earmolds, which are built to prevent feedback and falling out; half-shell earmolds, which only cover the bottom half of the concha bowl; skeleton earmolds, designed for comfort and semi-skeleton earmolds, similar to skeleton but without the back ring. Each of these styles is custom-molded to the patient’s ear for comfort and effectiveness. 
 Pediatric audiology is the study and treatment of hearing loss in infants, toddlers, and children. Our experts evaluate and treat children of all developmental stages. Our goal is to detect and treat hearing loss in children as early as possible. Since our audiologists work closely with our physicians, we can care for your child’s whole hearing health.
Pediatric audiology is the study and treatment of hearing loss in infants, toddlers, and children. Our experts evaluate and treat children of all developmental stages. Our goal is to detect and treat hearing loss in children as early as possible. Since our audiologists work closely with our physicians, we can care for your child’s whole hearing health.  Hearing aids are devices designed to help those with hearing loss hear, process and understand sound. There are many types of hearing aids such as behind-the-ear aids, in-the-ear aids, invisible in-canal hearing aids, extended-wear hearing aids, open-fit devices and bone-anchored hearing aids. Each works differently and is recommended by a doctor based on the patient’s degree of hearing loss, lifestyle and preference.
Hearing aids are devices designed to help those with hearing loss hear, process and understand sound. There are many types of hearing aids such as behind-the-ear aids, in-the-ear aids, invisible in-canal hearing aids, extended-wear hearing aids, open-fit devices and bone-anchored hearing aids. Each works differently and is recommended by a doctor based on the patient’s degree of hearing loss, lifestyle and preference.  One of the most common hearing testing methods in adults and older children is pure-tone audiometry testing. This test determines what volume of sound a patient can hear at different frequencies. This test is usually conducted with headphones, but sometimes a sound booth is used. The doctor presents a tone through the speakers, and the patient indicates whether or not they can hear it. This test establishes whether a patient is impaired from hearing specifically high or low tones.
One of the most common hearing testing methods in adults and older children is pure-tone audiometry testing. This test determines what volume of sound a patient can hear at different frequencies. This test is usually conducted with headphones, but sometimes a sound booth is used. The doctor presents a tone through the speakers, and the patient indicates whether or not they can hear it. This test establishes whether a patient is impaired from hearing specifically high or low tones.  Common ENT issues that affect children are tonsil infections, sinus infections, hearing loss, snoring, sleep apnea, stridor (noisy breathing), infections of the lymph nodes, epistaxis (nose bleeding), chronic cough, voice disorders, nasal blockage and allergies.
Common ENT issues that affect children are tonsil infections, sinus infections, hearing loss, snoring, sleep apnea, stridor (noisy breathing), infections of the lymph nodes, epistaxis (nose bleeding), chronic cough, voice disorders, nasal blockage and allergies.