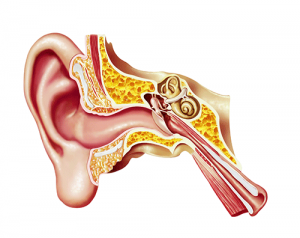
 Meniere’s disease is a disorder that attacks the inner ear and causes symptoms of vertigo (dizzy spells and nausea), hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears) and a plugged or pressurized feeling in the ears. Symptoms can last between twenty minutes and four hours. If left untreated, Meniere’s disease can cause permanent hearing loss. It generally affects people between the ages of 20 and 50.
Meniere’s disease is a disorder that attacks the inner ear and causes symptoms of vertigo (dizzy spells and nausea), hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears) and a plugged or pressurized feeling in the ears. Symptoms can last between twenty minutes and four hours. If left untreated, Meniere’s disease can cause permanent hearing loss. It generally affects people between the ages of 20 and 50.
Many believe Meniere’s can result from an abnormal volume of fluid in the inner ear when excess production or inadequate absorption occurs. Allergies or autoimmune disorders may also cause Meniere’s disease. Those with Meniere’s disease are more prone to experiencing fatigue and stress.
In order to diagnose the disease, your doctor will ask you about your history including frequency, duration and severity of symptoms. Then diagnostic tests will be performed. Hearing tests such as speech discrimination evaluations can determine if the affected ear is experiencing temporary or permanent hearing loss. Balance tests such as ENT or VNG may be performed to determine if the balance system is affected by the disease. Other tests can determine if fluid pressure or auditory brain stem response is abnormal. If these tests are positive, the patient likely has Meniere’s disease.
Although there is no sure cure for Meniere’s disease, some behaviors can help reduce symptoms. Your doctor may recommend a low salt diet and a diuretic, anti-vertigo medications, intratympanic injection of medications, air pressure pulse generator and/or surgery. Surgery is only recommended if vertigo attacks are not managed by alternative treatments or if the symptoms are disabling.
